Legal DNA Testing
Our lab methods exceed relationship testing standards and offer unparalleled accuracy in DNA reporting.
We test 40+ DNA markers, which is over 175% more than other DNA labs.
That's why we offer a 24-marker paternity test for legal and non-legal cases. That's 50% more markers than industry-standard.
For most of the relationship testing, we used a 46-marker test that's 187.5% more markers than industry-standard. If your test sample submitted is weak, we automatically upgrade to our 46-marker test at no additional cost. What does this mean for you? More markers translated for greater accuracy and reliability of test results. For the certainty and assuredness that you want and deserve, choose accurate and reliable forensic testing.
We take customer privacy very seriously and have built safeguards into every step of our DNA testing process. All sensitive personal information will be kept secure and treated as strictly confidential by our laboratory professionals' team.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
In genetics, a biomarker (identified as genetic marker) is a DNA sequence that causes disease or is associated with susceptibility to disease. They can be used to create genetic maps of whatever organism is being studied.
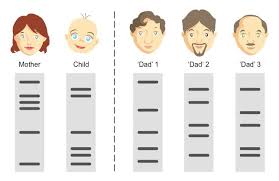
They're called microsatellites, simple sequence repeats (SSRs), short tandem repeats (STRs), or variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs). These are places in the DNA where a certain bit of DNA is repeated. ... You have 17 repeats on one chromosome and 18 on the other at D3S1358, a certain spot on a chromosome.
Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is the genetic material you inherit from your mother and father. Paternity refers to fatherhood. A DNA paternity test uses DNA, usually taken from a cheek swab, to determine whether a man is the child's biological father.
Genetically, you actually carry more of your mother's genes than your father's. That's because of little organelles that live within your cells, the mitochondria, which you only receive from your mother.
We do ask that you don't eat or drink anything for about an hour before collecting the DNA samples, and this is to keep food or anything else off the swabs. Eating or drinking before the collection can cause remnants to get on the swab with the DNA, degrading the sample.
Swabs are as accurate as blood. Epithelial cells contain exactly the same DNA as blood cells. In other words, these swab tests are more than 99.9% accurate, which is the same in case of blood samples as well.
Your genome is inherited from your parents, half from your mother and half from your father. The gametes are formed during a process called meiosis. Like your genome, each gamete is unique, which explains why siblings from the same parents do not look the same.
It is possible for twins to have different fathers in a phenomenon called hetero-paternal superfecundation, which occurs when two of a woman's eggs are fertilized by sperm from two different men. Ordinarily, a woman becomes pregnant because one of her eggs has been fertilized by sperm
Paternity testing with just a father and a child usually produces a high CPI and a very high Probability of Paternity (usually 99.99% or greater if he is the father). However, sometimes the matches between father and child aren't strong enough for conclusive results.
As we've learned, dads contribute one Y or one X chromosome to their offspring. Girls get two X chromosomes, one from Mom and one from Dad. This means that your daughter will inherit X-linked genes from her father as well as her mother. ... Remember, girls inherit two X chromosomes—one from mom, one from dad.